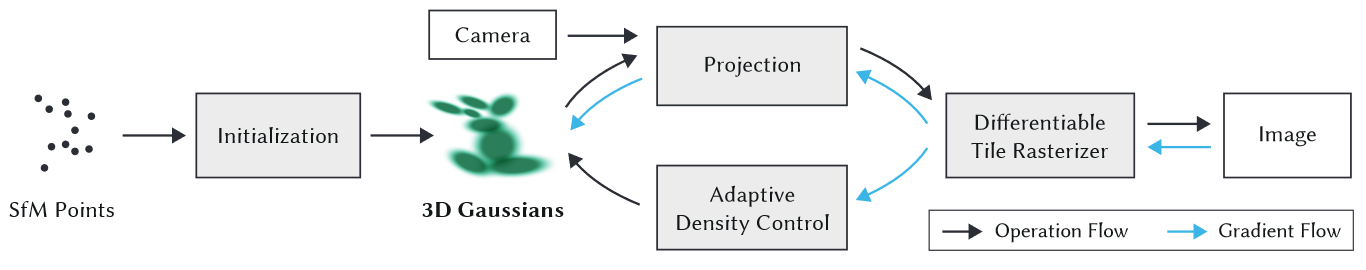
Mip-Splatting: Alias-free 3D Gaussian Splatting
3DGS在改变采样率或者改变焦距和相机距离时,会存在严重的膨胀效应和高频伪影
采样理论(奈奎斯特-香农采样理论)
对连续信号的采样频率至少是最大频率的两倍,所以在采样之前要对信号施加滤波。
3DGS中的Dilation操作
为了防止投影的2DGS小于一个像素,所以投影的2DGS进行了膨胀操作:
Sensitivity to Sampling Rate

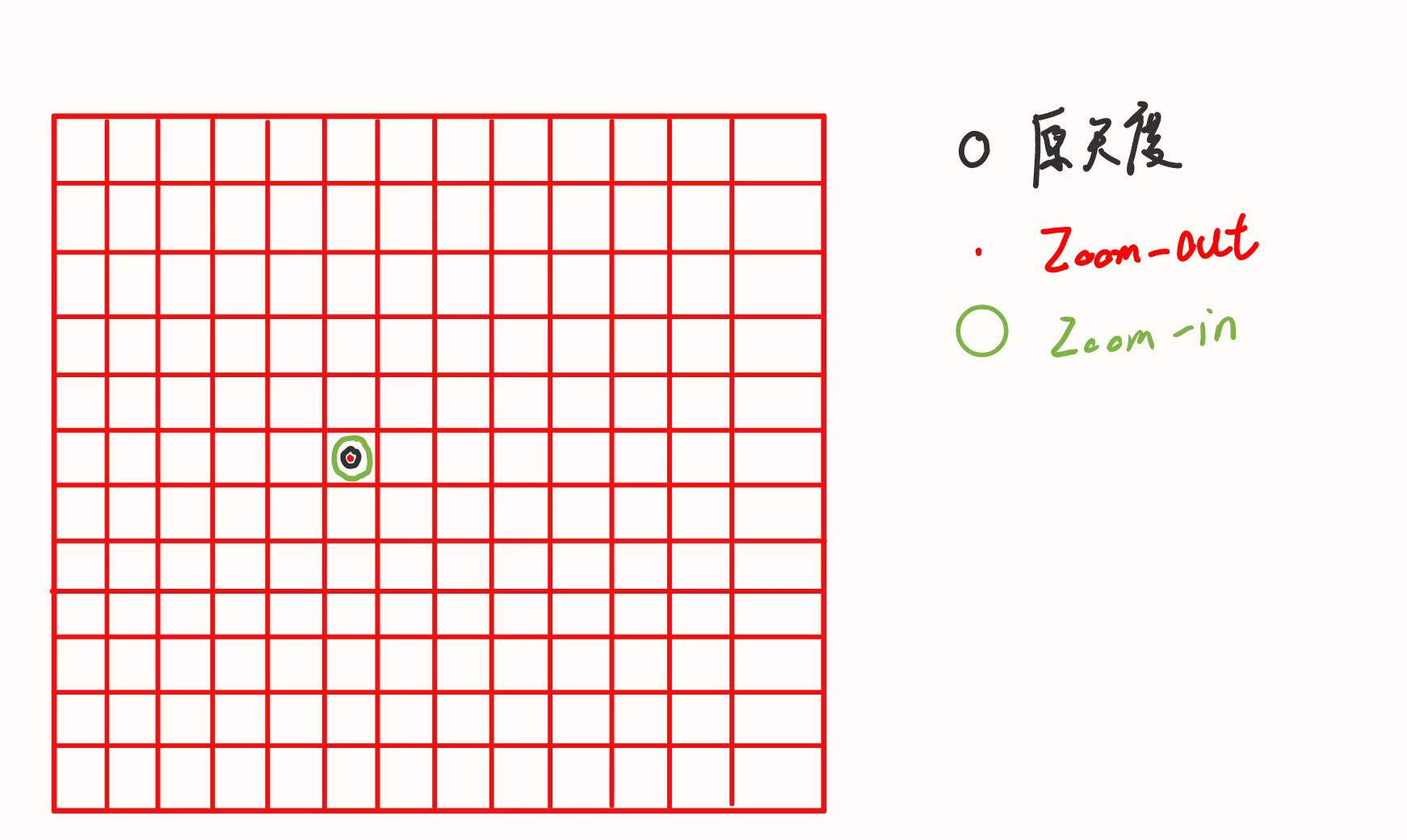
对于Zoom-out,原本的object在像素中的占比缩小了,所以为了要膨胀到一个像素的大小,施加的二维膨胀相较于原来更大
对于Zoom-out,原本的object在像素中的占比变大,所以膨胀到一个像素大小所需的二维膨胀就更小
it leads to erosion effects when zooming in or moving the camera closer. This is because the dilated 2D Gaussians become smaller in screen space. In this case, the rendered image exhibits high frequency artifacts, rendering object structures thinner than they actually appear as illustrated in Figure 1 (d).
Note that in (c), the area covered by the projection of the 3D object is smaller than a pixel, yet the dilated Gaussian is not attenuated, accumulating more light than what physically reaches the pixel. This leads to increased brightness and dilation artifacts which strongly degrade the appearance of the bicycle wheels’ spokes.
如果简单地放弃膨胀,重建复杂场景就需要更多的小高斯,这可能会超出GPU的容量,即使能够成功训练,也会导致锯齿现象。
Mip Gaussian Splatting
3D Smoothing Filter
焦距为$f$,在屏幕空间中采样间隔为1,当像素的采样间隔反向投影到三维世界当中,世界空间中在给定深度$d$下的采样间隔为采样频率的倒数:
对于高斯元$k$的最大采样率为:
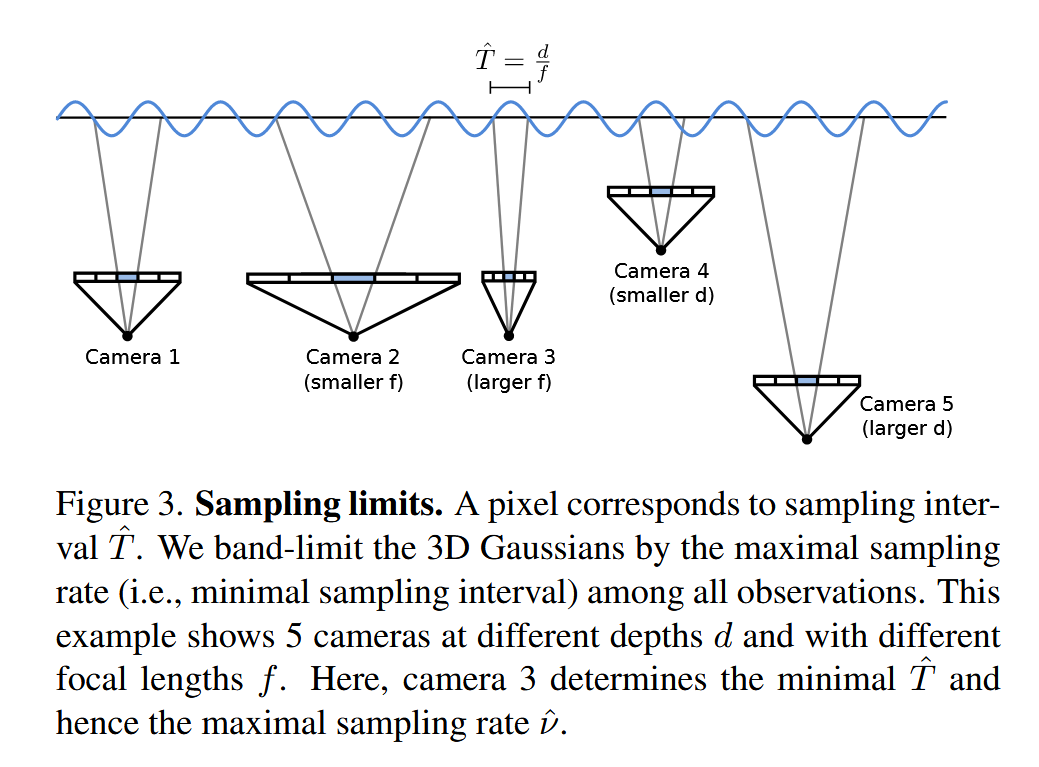
给定了最大采样频率之后,就可以通过一个高斯低通滤波来限制3DGS的最大频率:
2D Mip Filter
使用二维高斯滤波替换膨胀滤波: